Access and Decode BMW Motorcycle CAN Bus
How to access BMW's motorcycle CAN Bus network and decode messages
What is canbus
CAN bus (Controller Area Network) is a robust communication protocol used in vehicles and industrial systems to allow different devices, like sensors, controllers, and actuators, to communicate with each other efficiently without needing a central computer. It’s particularly popular in automotive systems because it’s fast, reliable, and allows multiple systems (like the engine control unit, dashboard, and airbags) to share information in real-time. Essentially, it enables the smooth and synchronized operation of many components in complex environments, like cars or most recently in motorcycles.
How getting data from the CAN Bus can be useful
Accessing a vehicle’s CAN bus opens up a world of possibilities for anyone looking to enhance their driving or riding experience. Whether you’re into cars or motorcycles, tapping into this network can allow you to create some really cool, personalized features.
One of the most popular projects is building custom dashboards or instrument clusters. By accessing real-time data like speed, RPM, fuel level, and engine temperature through the CAN bus, you can create a digital display or heads-up display (HUD) with platforms like Arduino or Raspberry Pi. Imagine seeing all the critical info you need on a custom screen you’ve designed yourself—perfect for giving your ride a tech-savvy upgrade.
Another great use of the CAN bus is data logging and performance monitoring. With a CAN bus reader, you can record real-time data while driving or riding, capturing everything from fuel efficiency to engine performance. Not only is this data useful for optimizing performance, but it also helps in diagnosing issues by logging fault codes. You can even visualize the data later to spot trends or fine-tune your vehicle’s behavior.
Lastly, remote vehicle monitoring is another exciting project. By pairing a CAN bus reader with a wireless device like an ESP32 with Wi-Fi or Bluetooth, you can build a system that lets you monitor your vehicle’s health from a distance. Set up alerts for things like low battery voltage or engine faults, and receive notifications on your smartphone, making sure you’re always in the loop, even when you’re away from your vehicle.
Locating the CAN Bus lines
Tapping into your vehicle’s CAN network is easier than you might think, with a few common spots offering direct access. The most convenient is the OBD-II port, found under the dashboard in most cars and motorcycles made after 2008. This port is great for reading basic data like engine diagnostics, speed, and fault codes, making it ideal for quick projects. However, it’s important to note that in many modern vehicles, the OBD-II port is often firewalled, meaning not all CAN messages pass through it. Some systems, like those for safety or infotainment, may not be accessible through this port.
For deeper access, you can tap directly into the ECU (Engine Control Unit), which handles critical vehicle systems. Though more advanced, this gives you greater control over the data, but you’ll need to identify the right CAN wires.
Another good spot is behind the instrument cluster, where the CAN signals for things like speed and RPM are easily accessible—perfect for building custom displays.
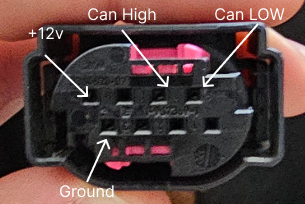
In my case there are un firewalled CAN Bus lines in a connector that’s under the seat where the alarm unit often plugs to, if your bike is fitted with the alarm unit you will need to make an adapter to allow to plug in the alarm unit at the same time as your CAN interface. This connector is part number #83300413581 in case you want to buy one for a more reliable connection.
This connector’s pinout is as follows:
In my particular motorcycle (2020 F900XR) the colors are:
| Wire Color | Description |
|---|---|
| Red and White | +12v |
| Black | Ground |
| Blue | CAN High |
| Gray | CAN Low |
Reading Messages
To read CAN bus messages on a computer, you’ll need a few essential tools: a CAN adapter to interface between the CAN network and your computer, software to interpret the data, and the proper wiring setup. We will start of by choosing an adapter, there are a few available models on the market at varying pricing points but I’ll be using the MKS CANable Pro, this adapter can come flashed either with slcan or candleLight, I’ll be using candleLight so if your adapter is not flashed with candleLight there’s a guide available on the canable official website. To interpret the data I will be using cangaroo, but you can also use savvycan with a custom plugin. Plug your can interface to your motorcycle according to the diagram presented above and then connect the can interface to your computer, after that open cangaroo and on the top bar go into Measurement->Start Measurement (F5), select your interface and set the baud rate to 500000kb/s, then turn on the ignition on the motorcycle and if everything is working as expected you should see the messages starting to come in.
Decoding Messages
After we’ve successfully started to read messages now comes the time to decode them, fortunately almost all of the messages have been decoded and can be found on this spreadsheet.
Creating a python application to read the real-time data
To make anything useful out of this data I will be creating a python dashboard, the source code for this dashboard can be found here. In order to use this example you will first need to connect you candleLight as a network device in linux, to do that run the following command:
sudo ip link set can0 up type can bitrate 500000After you’ve run this command a green light should appear on you can interface (if you are using CANAble), then clone the repository mentioned above and run ‘main.py’. I should also note that if your motorcycle is not an F900XR you might have to tweak the decoder functions to match the messages sent by your motorcycle.
Here’s a demo video:
Conclusions
In conclusion, the CAN bus is a vital communication protocol that allows different systems within a vehicle to share information efficiently, without needing a central computer. It plays a critical role in ensuring that modern vehicles operate smoothly and safely. By tapping into the CAN bus, you can unlock a range of possibilities, from building custom dashboards to monitoring real-time performance data, or even diagnosing issues remotely. With the right tools—like a CAN adapter, some software, and a bit of coding—you can transform raw data into useful insights or cool features for your vehicle.
On a future article I will cover how you can decode CAN messages using an ESP32 and even integrate your vehicle with home assistant. If you’re curious the here’s the repo for the mentioned project can be found here.
Thank you for reading and as always you can contact me trough my social media 😊.